Conjugated Linoleic Acid, widely known as CLA, encompasses a group of polyunsaturated fatty acids that hold a prominent place in the realms of health and fitness. Synthesized in the digestive tracts of grass-eating animals like cows and goats, this fatty acid is present in their meat and dairy products. CLA is not only recognized for its potential role in reducing body fat and augmenting lean muscle mass but also for its asserted impact on bolstering overall health through various metabolic pathways.
Its terminology, though, often permeates through the broader spectrum of nutrition, encapsulating its presence in certain oils, dairy products, and available supplement forms. While its benefits, predominantly in weight management, are often highlighted, the exploration into CLA also ventures into understanding its potential risks, ensuring that its use is balanced, informed, and aligns with individual health parameters and goals.
What does CLA stand for?
The acronym “CLA” stands for Conjugated Linoleic Acid. Despite its concise abbreviation, CLA symbolizes a complex group of chemical compounds, all of which are polyunsaturated fatty acids. Notably, it comprises at least 28 different forms, or isomers, which are structural variations of the same molecular configuration, each wielding its properties and impacts on the body.
It’s important to point out that while CLA stands as a singular term, its impact and functionality are deeply rooted in the multifaceted and complex interactions of its various isomers within the body. This depth ensures that the exploration into CLA is not only about understanding its general impact but also navigating through the specificities and nuances brought about by its different forms.
What are the functions of CLA?
Conjugated Linoleic Acid performs many functions in the human body, transcending from impacting metabolic rates to influencing the cellular membrane structure. One pivotal function includes its purported role in reducing adiposity, where it is thought to modulate the metabolic rate and direct the way the body stores and utilizes energy.
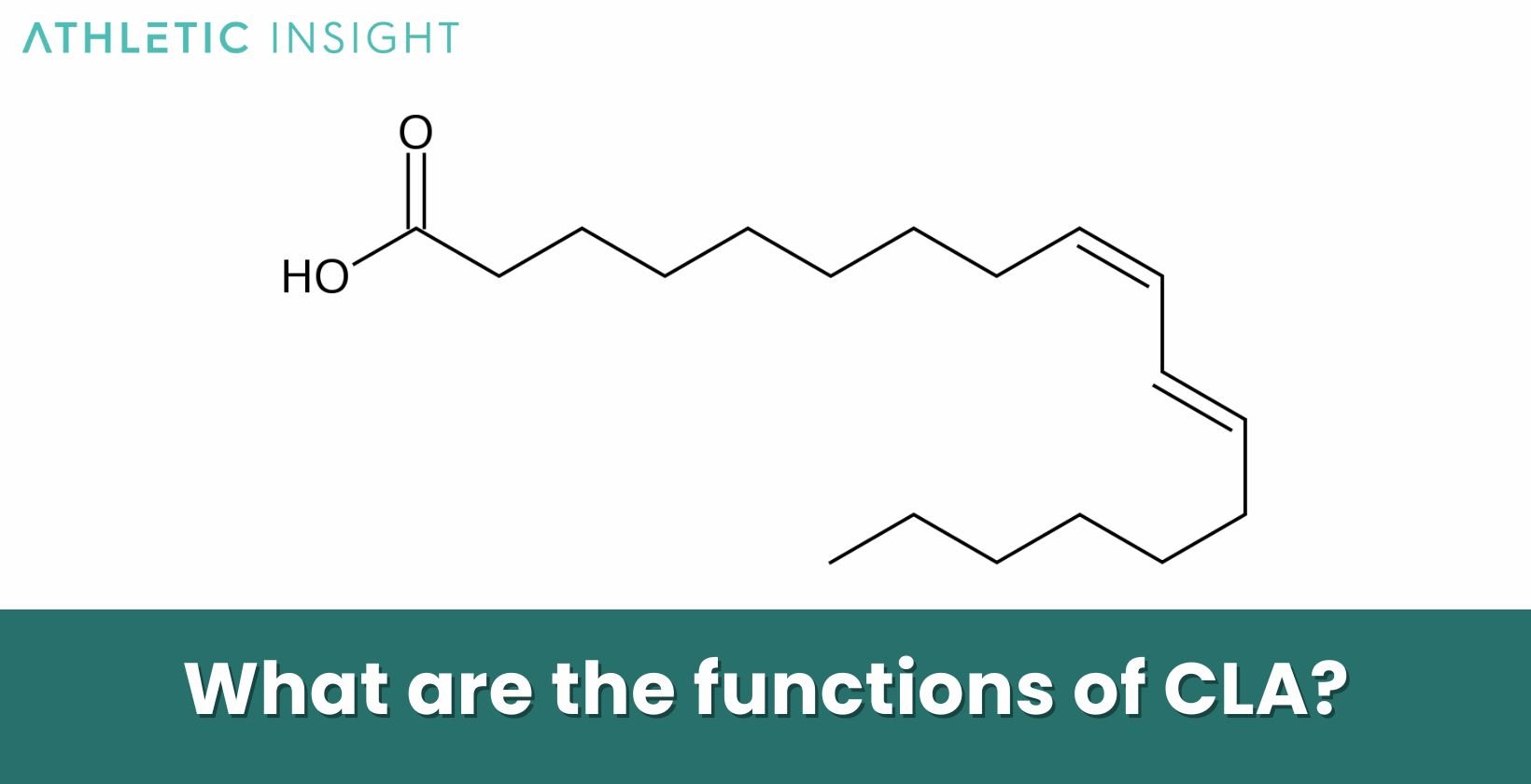
In addition, CLA also demonstrates its involvement in supporting immune system functionality, where its anti-inflammatory properties come into play, potentially mitigating undesirable inflammatory responses within the body.
The functionality of CLA also extends into influencing lipid metabolism, particularly in its potential to reduce triglyceride and cholesterol levels. In the realms of muscle metabolism, CLA seems to exhibit a supportive role in potentially aiding the maintenance of lean muscle mass, providing a critical framework in scenarios where muscle retention is paramount.
It’s also worth noting that the functions of CLA are backed by various research studies, albeit with results that sometimes present conflicting data, emphasizing the necessity for further research and scrutiny.
Who should use of CLA?
Individuals commonly integrate CLA into their regimen for its proclaimed ability to support weight management and immune system function. Particularly, those embarking on weight loss journeys or aiming to maintain lean muscle mass might utilize CLA supplements or focus on CLA-rich foods to potentially amplify their efforts.
Due to its anti-inflammatory properties, individuals with certain inflammatory conditions might also explore the utility of CLA, always under prudent professional advice to ensure alignment with their health profiles.
It’s important to understand that while CLA is often heralded for its benefits, its usage should always intertwine with comprehensive understanding and potentially under professional guidance, particularly for those with specific health conditions or goals. The eligibility to utilize CLA must account for individual health statuses, objectives, and any potential risks, to nurture an environment where its use is optimized and safeguarded.
Who should not use CLA?
Certain types of individuals should step back from using CLA to ensure their health remains uncompromised. Individuals with known allergies or sensitivities to CLA or any of its components should avoid it. It’s vital to keep in mind that if someone notices any unusual reactions after consuming CLA, like rash or breathing issues, immediate cessation and professional consultation are advised.
Pregnant or breastfeeding mothers should avoid CLA supplements due to limited research in these specific demographics. For that reason, it is best to consult with your primary care doctor before taking CLA.
What are the dietary sources of CLA?
Conjugated Linoleic Acid is naturally found in several dietary sources, mainly from animal products. Beef and dairy products, such as milk, cheese, and yogurt, are typically rich in CLA, providing a direct pathway to integrate this fatty acid into one’s dietary routine. These sources not only present a tangible CLA content but also offer additional nutritional benefits, such as protein and calcium, fostering a multiplex of nutritional support.

It’s also important to note that the quality and quantity of CLA in these food sources can depend on various factors like the diet and lifestyle of the animals from which they are derived. For instance, meats and dairy from animals that have been grass-fed or pasture-raised tend to contain higher levels of CLA, thus providing a more potent dietary source for individuals seeking to enhance their CLA intake through natural means.
What are the potential benefits of CLA supplementation?
There are many known benefits of CLA supplementation. One of the widely recognized advantages is its role in assisting weight management. Some studies indicate that CLA supplementation might help reduce body fat and enhance lean muscle mass, contributing to a more balanced body composition. Such an effect can be particularly beneficial for those navigating through weight loss journeys, presenting CLA as a potential ally in such endeavors.
Also, CLA is touted for its antioxidative properties, which means it might help shield the body’s cells from damage caused by unstable molecules known as free radicals. Such a role propels the utility of CLA beyond mere physical appearance enhancements, venturing into the arena of cellular health and longevity. However, it’s pivotal to note that while certain studies underscore these benefits, others render conflicting results, thus weaving a tapestry of continuous research and exploration in the scientific community.
What are the risks of CLA?
While CLA offers many appealing benefits, it is equally important to navigate through its associated risks with an informed understanding. Certain studies signal towards a possible impact of CLA in elevating liver fat. An increase in liver fat can pose risks, particularly for individuals with existing liver conditions or those susceptible to developing such issues, entwining CLA supplementation with potential health dilemmas in such scenarios.
Some individuals may also experience digestive issues, such as bloating or upset stomach, when consuming CLA supplements, particularly when initiated at higher doses. So, while CLA parades a variety of potential health benefits, a meticulous evaluation of its risks is required before immersing into its supplementation.
Are there any CLA supplement side effects?
Yes, CLA supplements can cause some side effects, warranting cautious consumption and a vigilant adherence to recommended dosages. Some individuals might encounter digestive disturbances, manifesting as an upset stomach or bloating, especially when they commence CLA supplementation. Navigating towards gradual dosage introduction and adhering to specified guidelines can often mitigate such effects, thereby harmonizing the integration of CLA into one’s dietary regime.
An additional side effect noted in certain studies is an increment in liver fat, which while subtle, begets a necessary caution for individuals with liver conditions. Fatigue and experiencing a decrease in metabolic rates are other potential side effects, thus infusing the CLA supplementation journey with the necessity for comprehensive awareness and perhaps periodic health check-ups to monitor its impact.
What is the contribution of CLA in exercise?
The landscape of exercise and physical exertion is often where CLA has been spotlighted, particularly for its supposed role in aiding fat reduction and augmenting lean muscle mass. The substance, within scientific examinations, has demonstrated a capacity to modulate the body’s fat-to-muscle ratio, thereby potentially enhancing the outcomes of regular physical activity. This role of CLA not only aligns with aesthetic goals but also bolsters physical performance and stamina, bridging the realms of appearance and functional capability in the physical context.
Also, by potentially assisting in reducing body fat and facilitating an increase in lean muscle, CLA can be perceived as a supportive agent in one’s exercise journey. Nonetheless, while the bridges to potential benefits are intriguing, it’s essential to understand that the efficacy and impact of CLA in exercise and weight management are still subjects housed within the corridors of ongoing research and discussion among scientists and health experts.
Can CLA help with weight loss?
Yes, CLA can help with weight loss. Research suggests that CLA, notably its trans-10, cis-12 isomer, may modestly decrease body fat and engender minor reductions in weight. The molecular mechanisms might involve modulation of fat metabolism, influencing the way the body stores and utilizes energy from food. Yet, it’s vital to underscore that while some studies affirm these outcomes, others present conflicting results, shrouding CLA’s efficacy in a veil of ongoing debate and investigation.
The holistic perspective on weight loss, inclusive of CLA, demands a balanced view that also considers diet, physical activity, and general lifestyle. While some may experience discernible effects with CLA supplementation, others might navigate through a less impactful experience. Therefore, it’s pivotal to approach its use with balanced expectations and perhaps envisage it as a potential supplementary aid within a broader weight management strategy, rather than a solitary solution.
What is CLA made of?
Conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) encompasses a group of chemical isomers of linoleic acid, which is a type of polyunsaturated fatty acid, specifically an omega-6 fatty acid. CLA is distinguished by the arrangement of double bonds in its structure, which orchestrates its chemical properties and subsequent biological activities. Naturally occurring CLA is synthesized in the digestive tracts of ruminant animals like cows and sheep, through the action of bacteria upon the linoleic acid derived from their diet. Subsequently, CLA is deposited in the muscles and milk of these animals.
Conjugated linoleic acid as a nutrient has, in a natural context, been part of human diets for millennia, found in food like beef and dairy. Still, the commercial CLA supplements encountered in today’s market often derive from sunflower or safflower oil, through a process that adjusts the positioning of the double bonds, yielding synthetic CLA. The discourse surrounding natural versus synthetic CLA also meanders through research circles, exploring potential differences in biological impact and efficacy between them.
What is the Best CLA Supplement?
Determining the “best” supplements can be somewhat subjective due to variations in user experiences and preferences; nonetheless, a few have garnered acclaim in the context of CLA supplements. Overall, the best CLA supplement is Sports Research Max Potency CLA 1250, which often finds a spot on various recommendation lists. This is due to its derivation from safflower oil and incorporation of non-GMO ingredients, catering to those prioritizing natural constituents.

Second, NatureWise CLA 1250 is often touted for its high potency and non-stimulating nature, which renders it a plausible option for individuals cautious of overstimulation. Third, BulkSupplements CLA Softgels have garnered attention for their affordability and bulk availability, providing a cost-effective approach to consistent supplementation.
When selecting a supplement, a thorough scrutiny of labels, third-party testing affirmations, and comprehensive research about the brand’s reputation is crucial to align the choice with personal health goals and ethical stances.
What to know before you use CLA?
Before incorporating CLA into your wellness regimen, acquaint yourself with several key considerations to ensure an informed and prudent approach. Recognition of your health status, potential allergies, and any pre-existing conditions serves as a foundational step.
Interactions of CLA with medications or other supplements already in use should also be meticulously investigated to sidestep unfavorable synergies. Verification of the authenticity and quality of the CLA supplement, through scrutinizing product reviews and ensuring it has undergone third-party testing, will stand you in good stead to minimize risks.
Engaging in dialogue with a professional can also facilitate a deeper understanding of the appropriate dosages and administration times that would be most efficacious, based on your unique physiological parameters and health objectives.
What is the best time to take CLA?
The best time to ingest CLA can depend largely on the individual objectives tied to its use. Some research indicates that taking CLA before or during meals can optimize its efficacy, particularly when weight management is the target. In this context, assimilating CLA with dietary fats might enhance its absorption and thereby, potentially amplify its impact on fat metabolism.
On the contrary, if stomach sensitivity is noted, taking CLA with meals might alleviate potential discomfort and facilitate smoother digestion, which may be particularly pivotal for those with sensitive digestive systems.
Nonetheless, the timing should also coalesce with personal routines and physiological responses to ensure adherence and comfort in its use. Taking note of body reactions, energy levels, and any nuanced shifts in wellbeing post-ingestion at different times can assist in tailoring a schedule that’s symbiotic with individual rhythms and lifestyle.
What is the average CLA dosage daily?
Determining an appropriate daily dosage of CLA is a nuanced process, anchored in various factors including individual health goals, body weight, and overall health status. Studies exploring CLA, particularly in the context of weight management, have deployed dosages ranging from 3.2 to 6.4 grams per day, and these figures often serve as a reference point in general discussions about CLA dosage. It’s pivotal to observe that while some individuals may notice benefits at lower dosages, others may require a higher intake to discern tangible changes.
Explicit guidelines regarding CLA dosages might fluctuate between brands and specific formulations. Therefore, it’s important to stick to the manufacturer’s instructions.
How often should I take CLA?
You should take CLA supplements daily, which is a common guideline found on many supplement labels. The idea behind daily intake is to maintain a consistent level of CLA in the system, fostering an environment where its potential effects on fat metabolism or other targeted outcomes can be optimized. Splitting the total daily dosage into smaller portions and spreading them across the day, often in tandem with meals, has been a commonly adopted strategy among users and researchers alike.
Ensuring that CLA is taken consistently is thought to be a key in unlocking its potential benefits, particularly where metabolic and body composition changes are sought. Observing adherence to suggested intake frequencies and pairing that with a balanced diet and lifestyle practices may unfold as an essential strategy in fully exploring what CLA supplementation might offer to an individual’s wellness journey.
How long does it take for CLA to work?
Studies suggest noticeable changes might start to surface within a window of several weeks to a few months of consistent CLA supplementation. It’s essential to approach this with an understanding that response times can diverge significantly across individuals, influenced by their unique physiological makeup and lifestyle.
Patience, consistency, and keen observation become pivotal in gauging the effectiveness of CLA. Tracking changes, both subtle and pronounced, in correlation with CLA intake may provide insights into its working timeline within the body, enabling adjustments and ongoing, informed decision-making regarding its continued use.
What is the precaution of CLA?
Initial considerations and precautions of taking CLA should hinge on an individual’s health status and any underlying conditions that might interact with CLA in unexpected ways. Especially for those with pre-existing conditions or those on certain medications, understanding how CLA might interact with various biological processes is fundamental in circumventing unintended consequences. Hence, pre-supplementation discussions and regular health check-ins during its use can function as precautionary steps, ensuring that the journey with CLA is navigated with safety at the forefront.
What should I refrain from while taking CLA?
Conjugated Linoleic Acid (CLA), while being investigated for various potential benefits, can also interact with specific substances or conditions, which necessitates caution in its use. Some medications or substances might either augment or diminish the effects of CLA, or alternatively, CLA might alter the effectiveness of other medications. Certain medications, such as anticoagulants or antiplatelet drugs, deserve particular attention as CLA can, in some instances, influence blood clotting mechanisms.
Refraining from combining CLA with substances or practices that could jeopardize its safety or effectiveness remains pivotal. Once again, a healthcare professional can guide through this complex web, ensuring that CLA supplementation is tailored in a way that is mindful of these potential interactions and keeps the user’s health and safety at the forefront of their supplementation journey.
Can vegetarians and vegans take CLA?
Yes, vegetarians and vegans can take CLA but it is important to check the labels first. While CLA is naturally found in animal products like meat and dairy, synthetic forms of CLA, often used in supplements, can sometimes be suitable for those adhering to a vegetarian or vegan lifestyle. It’s pivotal to scrutinize supplement labels to decipher the origin of CLA and determine if it aligns with dietary practices.
For those adhering strictly to vegan principles, sourcing a plant-based CLA supplement derived synthetically and not from animal sources becomes crucial. Specialized supplements designed to cater to vegetarians and vegans are available, providing a path to explore the potential benefits of CLA without deviating from dietary convictions.
Is there an age limit for CLA supplementation?
Yes, age can be a determining factor in the appropriateness of CLA supplementation. Typically, CLA supplements are not recommended for children unless under specific medical advice, as the research into its effects on developing bodies remains in its infancy. Adults of various age brackets might also experience differential effects and efficacy with CLA, so a one-size-fits-all approach is discouraged.
Specific age groups, such as the elderly, might also have unique considerations that impact the safety and efficacy of CLA supplementation, such as interactions with medications or potential effects on muscle mass. Here too, dialogue with healthcare providers ensures that age-appropriate advice and precautions are heeded, safeguarding against potential missteps in CLA use across different age demographics.



